Clear Nails, Healthy Feet: Early Detection, Effective Treatment
At Alliance Laboratories, we specialize in the accurate diagnosis of onychomycosis (nail fungal infection) by identifying specific fungal pathogens. Our testing utilizes advanced molecular techniques to provide precise and rapid results, ensuring that patients receive the most effective treatment for their condition. Nail fungal infections can be persistent and challenging to treat, making accurate diagnosis critical for successful management. By leveraging our state-of-the-art technology, we can detect a wide range of fungal species, helping healthcare providers develop targeted treatment plans that improve patient outcomes and promote healthier nails.
Importance of Nail Fungal Testing
Accurate Diagnosis: Proper testing ensures the correct identification of the specific fungal species responsible, allowing for targeted and effective treatment.
Prevent Complications: If left untreated, nail fungal infections can lead to more severe issues, such as secondary bacterial infections and permanent nail damage.
Improve Quality of Life: Treating nail fungal infections promptly can alleviate pain, improve nail appearance, and restore your confidence.
Our Advanced Testing Methodologies
We use state-of-the-art diagnostic techniques to provide precise and reliable testing for nail fungal infections:
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Stains
Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS) Stains
What is PCR?
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies small DNA segments into millions of copies, enabling detailed analysis from minimal samples.
It involves:
- denaturation – heating DNA to separate strands
- annealing – binding primers to DNA
- elongation – extending new DNA strands
Essential in medical diagnostics, forensic science, and research, PCR detects pathogens, identifies genetic mutations, and analyzes DNA in detailed studies. PCR’s ability to provide rapid, accurate genetic analysis has revolutionized the biological sciences, making it a fundamental tool in diagnosing diseases, solving crimes, and advancing genetic research.

Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Stains
Hematoxylin: This dye stains the nuclei of cells blue or dark purple. Hematoxylin is a basic dye that binds to basophilic substances, which are those that are negatively charged, such as nucleic acids in the nucleus.
Eosin: This is an acidic dye that stains the cytoplasmic part of the cell and other tissue structures in various shades of pink and red. Eosin binds to eosinophilic (acidophilic) components, which are generally positively charged, like most cytoplasmic proteins.
H&E staining provides a clear view of the tissue structure, helping pathologists assess the arrangement and state of cells, and recognize patterns that might indicate a disease. It is usually the first step in identifying different types of tumors, inflammatory conditions, and infections. Depending on its findings, pathologists may recommend immunohistochemistry or molecular tests, to gather more specific information.
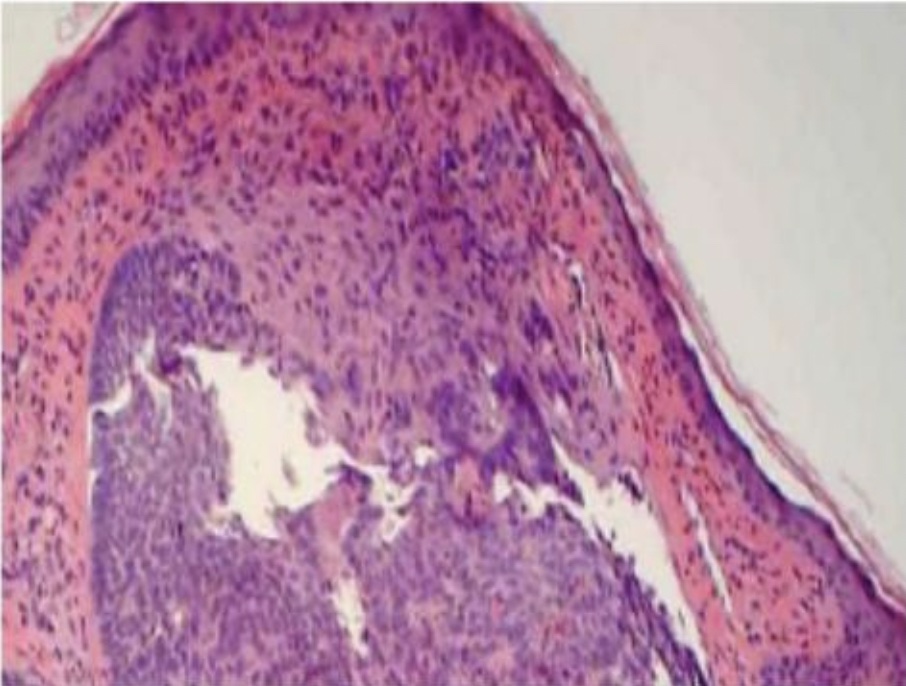
Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS) Stains

