What is Cytology Testing?
Cytology testing, also known as cytopathology, is a branch of pathology that involves the examination of cells from various body sites to diagnose diseases and conditions. It is widely used to detect cancer, precancerous conditions, and other abnormalities. The main feature of cytology is its focus on individual cell samples, unlike for example histology, which studies tissues.
Discover Our Cytology Methodologies
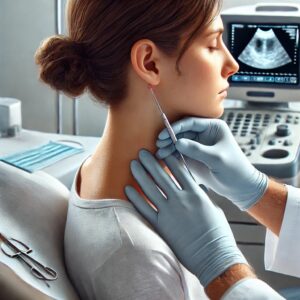
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
A minimally invasive procedure where a thin, hollow needle is used to extract cells from lumps or masses, often in the breast, thyroid, or lymph nodes.
The collected cells are then examined under a microscope to identify any abnormalities.
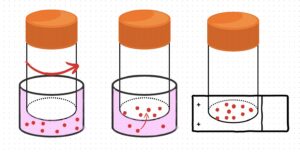
Cytocentrifugation
A technique that concentrates cells from body fluids (e.g., urine, cerebrospinal fluid) onto a slide for microscopic examination. This method enhances the detection of abnormal cells by creating a thin, uniform layer of cells.
Cytocentrifuge preparation outperforms the ordinary centrifuge in terms of cell yield, well-preserved cell morphology, and ability to pick up malignant cells, hence enhancing its sensitivity and improving its diagnostic use.

Liquid-Based Cytology (LBC)
Cells are collected in a liquid medium rather than on a glass slide, allowing for better preservation and easier processing.
The sample can be filtered and spread uniformly, reducing the presence of artifacts and improving diagnostic accuracy.
Pap Smear
Primarily used in gynecological cytology to detect cervical cancer and precancerous conditions.
Cells are scraped from the cervix and examined for abnormalities under a microscope.
Importance of Cytology Testing
Cytology testing plays a critical role in early disease detection, diagnosis, and management. It is a key tool for healthcare providers in identifying and treating conditions promptly, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
