Understanding Skin Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnostic Services
Skin cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer worldwide, but it is also one of the most preventable. Understanding the signs, causes, and methods for diagnosing skin cancer can significantly enhance treatment outcomes and potentially save lives. Our dermatology services play a vital role in both detection and management of skin conditions. Here’s what you need to know about skin cancer.
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer occurs when mutations develop in the DNA of skin cells, primarily due to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, causing the cells to grow uncontrollably. There are three primary types of skin cancer, each with distinct characteristics:
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): The most common form, appearing as pearly or waxy bumps or as flat, flesh-colored or brown scars.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): Often found on sun-exposed areas like the ears, face, and hands, manifesting as firm, red nodules, or flat lesions with a scaly, crusted surface.
- Melanoma: The most severe form, known for its ability to spread deeper into the body. It appears as a large brownish spot with darker speckles, or as a mole that changes in color, size or feel.
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
The symptoms vary depending on the type, but commonly include:
- New growths or sores that do not heal.
- Changes in existing moles or spots.
- Itchy or painful lesions.
Regular self-examinations and professional skin evaluations are crucial for early detection, particularly for individuals with high-risk factors.
Causes of Skin Cancer
The primary cause of skin cancer is exposure to UV radiation from the sun and tanning beds. Other risk factors include:
- Having fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes.
- A history of sunburns or excessive sun exposure.
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A large number of moles or freckles.
Diagnosing Skin Cancer:
Diagnosis involves a biopsy procedure where a small sample of the suspicious skin is removed and sent for testing. At ALLIANCE™, we employ these techniques to diagnose skin cancer accurately:
H&E Staining:
- Hematoxylin: This dye stains the nuclei of cells blue or dark purple. Hematoxylin is a basic dye that binds to basophilic substances, which are those that are negatively charged, such as nucleic acids in the nucleus.
- Eosin: This is an acidic dye that stains the cytoplasmic part of the cell and other tissue structures in various shades of pink and red. Eosin binds to eosinophilic (acidophilic) components, which are generally positively charged, like most cytoplasmic proteins.
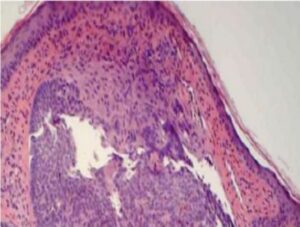
Basal Cell Carcinoma Identified under H&E Staining
Importance of H&E Staining:
H&E staining provides a clear view of the tissue structure, helping pathologists assess the arrangement and state of cells, and recognize patterns that might indicate a disease. It is usually the first step in identifying different types of tumors, inflammatory conditions, and infections. Depending on its findings, pathologists may recommend immunohistochemistry or molecular tests, to gather more specific information.
SOX-10 immunohistochemistry testing:
SOX-10 (SRY-related HMG-box 10) is a transcription factor that is essential in the development of neural crest cells, which give rise to a variety of cell types including melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment in the skin. It is expressed in normal melanocytes and in most melanocytic tumors, including melanoma. This makes SOX-10 a sensitive marker for melanoma, which means it can help identify melanoma cells in biopsy samples.
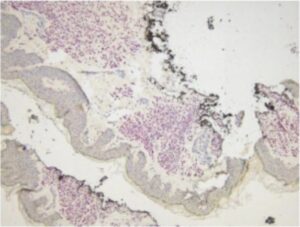
SOX-10 Staining
How SOX-10 Immunohistochemistry Works
In SOX-10 immunohistochemistry, an antibody specifically designed to detect the SOX-10 protein is applied to tissue samples. This antibody is linked to a dye to visualize it under a microscope. The presence of SOX-10 is indicated by the staining of the tissue where the antibody binds to the protein.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of skin cancer can drastically improve the prognosis and minimize the need for extensive and invasive treatment. ALLIANCE™ services support dermatologists by providing quick and accurate testing results, ensuring that patients receive the most effective care promptly.
Conclusion
Awareness and early diagnosis are key in the fight against skin cancer. Regular self-exams and professional screenings are crucial, especially for those with increased risk factors. At ALLIANCE™, we are committed to providing exemplary dermatology diagnostic services to aid in the timely detection and management of skin cancer. Protect your health by scheduling a skin examination today and ensure that any changes in your skin are evaluated promptly.
